Kidney Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, Preventive Measures
Kidneys are vital to having a wholesome healthy body. They are mainly responsible for filtering waste products, excess water, and different types of impurities out of the blood. These toxins are stored in the bladder and then removed during urination. The kidneys also regulate pH, salt, and potassium levels in the body. They produce hormones that regulate blood pressure and control the production of red blood cells. The kidneys even activate a form of vitamin D that helps the body absorb calcium.
Ten percent of the world’s population suffers from chronic kidney diseases. Millions of these affected people die every year due to the unfortunate fact of not having access to affordable treatment. In 2017, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) resulted in 1.2 million deaths and was the 12th leading cause of death worldwide. Unfortunately, kidney diseases have not received as much public attention as the extent of the problem deserves. The exact numbers suffering from chronic kidney diseases are not published by health departments in India. In India, 800 persons per million population are affected by CKD and 200-300 persons per million population are affected by End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). The exact numbers are unknown as negligible data has been published so far. The CKD registry, established by the Indian Society of Nephrology, will be hopefully useful in providing better data in future.
The most common form of kidney disease is CKD. Kidney stones are another common kidney problem. Glomerulonephritis, Polycystic kidney disease, Urinary tract infections are some of the other common diseases that affect our kidneys. However, if left untreated, these infections can spread and cause kidney failure.
CKD is a long-term condition that doesn’t improve over time. India has seen a significant increase in prevalence of CKD. It is currently one of the most commonly occurring non-communicable diseases in India. High blood pressure is considered to be the most common cause of CKD. High BP increases the pressure on the glomeruli (the tiny blood vessels in the kidney where blood is cleaned). Over a prolonged period of time, the increased pressure damages these vessels and kidney functions begin to decline. The function of kidneys is eventually impaired to the point where they aren’t able to perform their job. In this case, a person would need to go on dialysis. Dialysis filters extra fluid and waste out of the blood. Dialysis can help treat kidney disease but it can’t cure it. A kidney transplant may be another treatment option depending on various conditions.
In population based studies, the other most common cause of CKD is diabetes. Diabetes is a set of illnesses that cause excessive blood sugar. Over time, the increased level of sugar in the blood damages the blood vessels in the kidneys. Then, the kidneys are not able to clean the blood properly which eventually results in kidney failure due to overload of toxins in the blood.
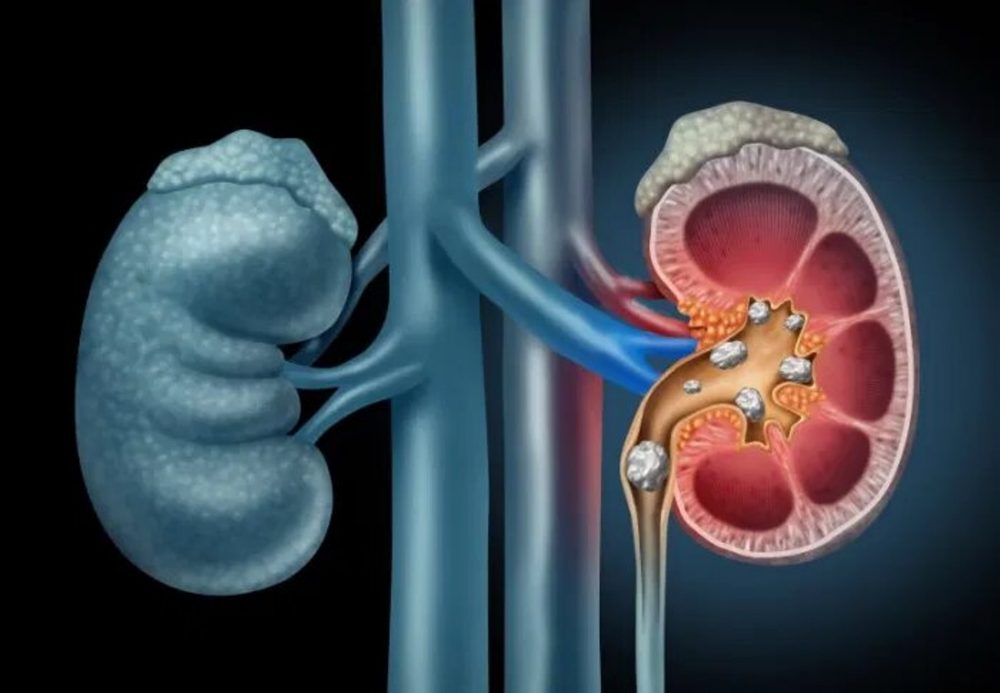
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside kidneys. Diet, excess body weight, some medical conditions, and certain supplements and medications are among the many causes of kidney stones. Kidney stones can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Passing kidney stones can be quite painful, but the stones usually cause no permanent damage if they’re recognised timely.
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the glomeruli. Glomeruli are extremely small structures inside the kidneys that filter the blood. Cause of glomerulonephritis can be infections, drugs, or congenital abnormalities (disorders that occur during or shortly after birth). It often gets better on its own.
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that causes numerous cysts (small sacs of fluid) to grow in the kidneys. These cysts can interfere with kidney function and cause renal failure.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections in any part of the urinary system. Infections in the bladder and urethra are the most common. They are easily treatable and rarely lead to more health problems. However, if left untreated, these infections can spread to the kidneys and cause kidney failure.
Symptoms
Kidney disease is a condition that can easily go unnoticed until the symptoms become severe. Some of the common symptoms include fatigue, feeling cold even in a warm room, shortness of breath even when there is no physical exertion, feeling faint and dizzy. Anaemia caused due to kidney failure results in the brain not getting sufficient oxygen, and this can cause dizziness or weakness, inability to think clearly, memory problems or trouble with concentration. Itchiness is another symptom caused due to build-up of wastes in the blood. This can also cause swelling in the hands or the feet – kidney failure leads to excess fluid build-up in the body, causing swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, and hands, swollen or puffy face. Upset stomach, nausea, vomiting due to severe build-up of wastes in the blood (uremia), frequent urination, particularly at night, pressure or difficulty in urinating, brown, red, or purple urine – the urine may contain blood – are other symptoms.
Diabetes is a major risk factor for kidney disease. Diabetes may damage nerves, and this can cause difficulty in emptying the bladder. The pressure from a full bladder can injure the kidneys, or cause an infection. High blood pressure is also a risk factor for kidney diseases. Patients with heart diseases are also at higher risk of developing kidney disease.
Prevention
Manage Blood Sugar Level: Blood sugar levels can be influenced by several factors, including those out of a person’s control such as hormones, illness, or stress. Over time, high blood sugar levels can cause blood vessels inside the kidney to become narrow and clogged and can cause damage to the blood vessels and harm the kidneys. If you have diabetes, the best way to protect your kidneys is to positively influence your blood sugar levels as best you can. Your treatment plan may include changes to your diet, exercise, and medicine to lower your blood sugar levels.
Manage Blood Pressure: If your blood pressure remains high, your doctor may advise you to take medicine. Making simple tweaks to your lifestyle, including lifestyle changes, can prevent or control high blood pressure. Eating a diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy products and skimps on saturated fat and cholesterol can lower your blood pressure. Include citrus foods in your diet and avoid salt, red meat, pizzas, pickles, canned soups, fatty and sugary products. Here in Kashmir, totally avoid salted tea as morning tea or have it on alternate days. It is important to get your blood pressure checked regularly – at least once every 6 months, and more often if you have high blood pressure.
Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet plan, such as the Mediterranean Diet and the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) Diet, can help lower blood pressure and blood lipids (fat in the blood). These eating plans include fresh fruits and vegetables, fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products, whole grains, fish, poultry, beans, seeds, and nuts. They also have less sodium, sugars, fats, and red meats.
Exercise: It can help you keep a healthy weight, control blood pressure and cholesterol, build strength and endurance, and lower your chances of getting diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease. There are many types of exercises that can help you stay healthy, including household chores, playing a sport, or aerobic exercises (swimming, biking, climbing stairs, or hiking). You can hit the gym or engage in morning or evening walks and jogging.
Limit Alcohol and Avoid Smoking: Drinking too much alcohol can raise your blood pressure. It also adds extra calories, which may cause weight gain. Both of those raise your risk of kidney disease. Cigarette smoking raises your blood pressure and puts you at higher risk of kidney disease and heart diseases. If you do not smoke, don’t start at any cost. If you do smoke, quitting will lower your risk for kidney disease. You can talk with your health care provider for help in finding the best way for you to quit. Don’t let anyone smoke near you in at least a radius of 1 metre.
Do not overuse painkillers: Using too many pain medicines called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen) may cause kidney disease. Long-term use of NSAIDs, especially at high doses, reduces the blood flow to the kidney which causes harm to kidney tissue.
Lack of specialist doctors, proper machines, and costly treatment are serious issues in management of kidney diseases. Africa is seeing a rise in kidney diseases for the last decade due to lack of machines and specialist medicos. Experts say that high blood pressure, high intake of sugar, smoking, taking less fluids, and use of pain killers are the main reasons behind kidney failures. The government must establish more infrastructure in hospitals to manage and treat kidney diseases. The government should also build enough public gyms and parks in rural areas to motivate more people towards daily exercises. People must be made aware about kidney diseases and effective preventive measures.

