

Zambia
Zambia, in southern Africa, is a landlocked country of rugged terrain and diverse wildlife, with many parks and safari areas. On its border with Zimbabwe is famed Victoria Falls – indigenously called Mosi-oa-Tunya, or "Smoke that Thunders” – plunging a misty 108m into narrow Batoka Gorge. Its population is 14 million people and GDP per capita of USD 1,844.
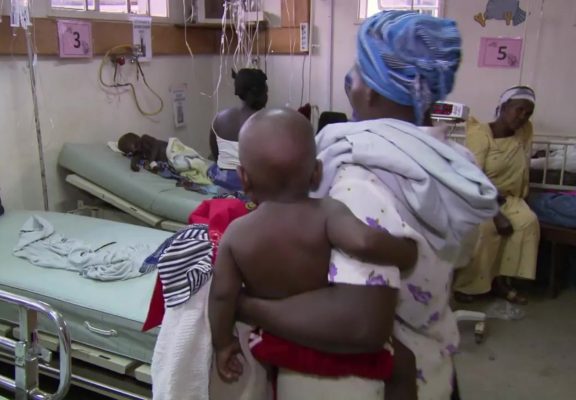
Zambia has shown strong growth in the last decade, reaching lower-middle-income status. The government contribution to the health sector has doubled between 2011 and 2014 and is expected to increase further. However, the health sector continues to be dependent on external resources, which accounted for 30-40 percent of health expenditure in recent years. Zambia has a serious AIDS epidemic and the country is working to strengthen prevention, care and support for people living with HIV. Malaria is endemic and is the leading cause of illness and death, but the country has made impressive progress by reducing malaria cases and deaths. TB is a major threat, and the risk of infection and co-infection with HIV are very high. The Zambia TB program aims to reduce illness, death and the socio-economic burden associated with TB through the expansion of treatment, improved laboratory services to ensure prompt and accurate diagnosis, and the scale-up of an initiative that links voluntary counselling and testing for HIV with TB case-finding and treatment.
AHO PRIORITIES FOR HEALTH DELIVERY PLAN IN ZAMBIA
- Health status of women and children.
- Access to quality health care, particularly for the poor with an emphasis on prevention and promotion through strengthened primary care.
- Procurement and delivery of drugs and medical supplies.
- Efficiency of health services/Facility rationalization strategies/Management capacity.
- Work terms and conditions for health personnel.
PROGRAMMES & PROJECTS
1. DISEASE PREVENTION AND CONTROL
PURPOSE
To strengthen the capacity of national authorities to control communicable and noncommunicable diseases
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Program for the Prevention of Communicable Diseases strengthened.
- Program for the Control fo Noncommunicable Diseases strengthened.
- Implementation of Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses strengthened in all regions.
- National Expanded Program on Immunization strengthened.
- Capacity to monitor health situation strengthened by improving the quality of data and timeliness of reporting.
- Project on disease prevention and control managed effectively.
2. MANAGERIAL PROCESS FOR NATIONAL HEALTH DEVELOPMENT
PURPOSE
To administer international technical cooperation for health effectively
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Delivery of technical cooperation enhanced through the efficient and effective management of the AHO office.
- Technical cooperation program delivered through the effective and efficient management of information systems and infrastructure.
- Opportunities provided for staff development in response to increased needs for expertise in their respective areas of work.
- Preventive maintenance conducted on office buildings, equipment, and vehicles.
- Donor coordination meetings on health convened at least twice a year.
- Development of the virtual health library supported.
3. HEALTH SYSTEMS AND SERVICES DEVELOPMENT
PURPOSE
To strengthen the capacity of the Ministry of Health to develop and implement health systems and services
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Strategies implemented to strengthen the steering role of AHO.
- Quality assurance programs developed for health services.
- Programs developed to improve oral and eye health and the health.
- Increased capacity of AHO to monitor and regulate the pharmaceutical system.
- Project effectively managed.
- Quality projects
4. HEALTH OF SPECIAL GROUPS
PURPOSE
To enhance the capacity of public, nongovernmental, and community-based organizations to apply health promotion strategies
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Capacity to establish and expand network of health promoting schools strengthened.
- Capacity for delivering maternal and perinatal health care services strengthened.
- Capacity for addressing health needs of vulnerable groups strengthened at the national and regional levels.
- Capacity for planning, implementing, and evaluating the healthy municipalities and communities strategy strengthened.
- The development of mental health services strengthened at the national and regional levels.
- Capacity for planning and implementing social communication strategies enhanced to promote healthy lifestyles
- Project effectively managed.
5. HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT
PURPOSE
To increase national capabilities to address environmental health issues (promoting healthy spaces, pollution control, and environmental protection).
EXPECTED RESULTS
- The National EH System improved through institutional strengthening.
- Conceptual and analytic capabilities strengthened in environmental risk management and assessment.
- Public awareness and community participation increased on environmental health issues.
- Leadership promoted on environmental health.
- Project coordinated.
RESOURCES (USD)
AHO ZAMBIA 2020 (USD million)* based on 2017 population of 17.09 million, World Bank
| SO | BUDGET ITEM | AMOUNT* |
| 1 | Combating communicable diseases |
284 |
| 2 | Tackling non communicable diseases |
300 |
| 3 | Addressing determinants of health & risk factors |
290 |
| 4 | Modernising health system and health service |
280 |
| 5 | Improving preparedness, surveillance and response |
285 |
| 6 | Developing good governance & corporate services |
270 |
| Total |
1,709 |
AHO estimates that it needs to spend at least USD100 per capita on health to meet the basic health needs of the people in Africa. This is too far below developed countries e.g. in England it is US$1,300 per capita (2017)

