

Benin
Benin is a French-speaking West African country. It has a population of 10.32 million people (2013). It has a GPD per capita of USD 804.69 and GPD of USD 8.307 billion.
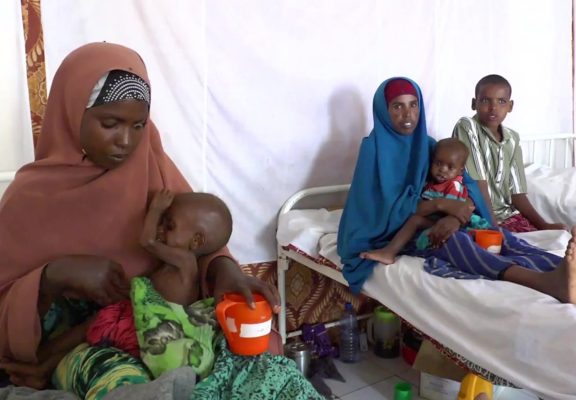
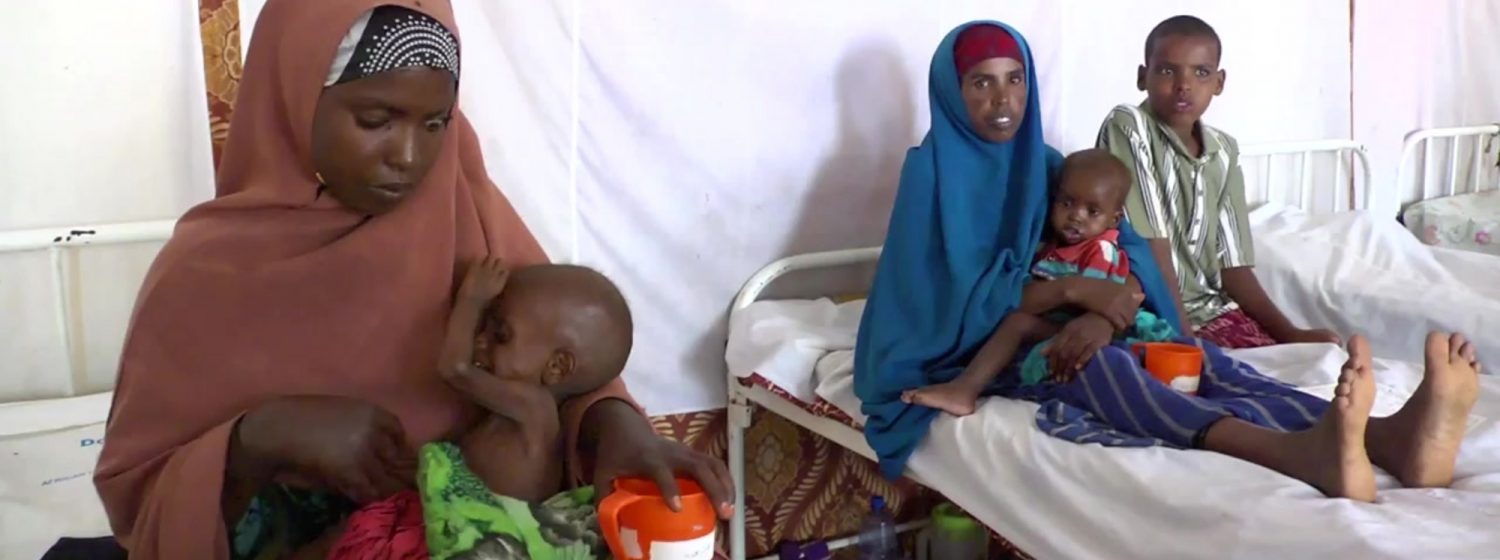
Benin is a West African country where poverty is widespread: 37 percent of the population lives on less than $1.50 per day. Malaria, HIV and tuberculosis are the three priority diseases in terms of public health. Malaria is the number one killer of children under-five and is a common condition afflicting many mothers and pregnancies each year. Since 2011 the Benin government has implemented a new policy which provides for free malaria services (prevention and treatment) for children under five, pregnant women and the most vulnerable. In 2014 Benin reached universal coverage through a mass campaign of bed net distribution mostly procured through the Global Fund. Health system strengthening has been a key health priority through the support of four donors: the World Bank, the Belgian Technical Cooperation, GAVI and the Global Fund. The objective is to improve the coverage and the quality of health care services throughout the country.
AHO PRIORITIES FOR HEALTH DELIVERY PLAN IN BENIN
- Health promotion and the prevention of risks and threats to individuals, families, and the community.
- Guaranteeing access to comprehensive care, with high-quality health services and an equity approach.
- Strengthening the steering role of AHO in health sectoral management.
- Decentralisation and modernisation of the sector through new management and financing modalities.
- Development and execution of human resources development policies.
PROGRAMMES & PROJECTS
1. DEVELOPMENT, MANAGEMENT, AND COORDINATION OF THE PROGRAMMES
PURPOSE
To create and maintain optimal conditions for technical cooperation through a respectful dialogue with the authorities, effective communication with public health actors, a continuing search for synergy in cooperation activities, human resources development, and rational use of human, financial, and technology resources.
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Strengthening of a measurable, continuous process of internal dialogue/coordination/articulation among team members and with third parties, such as national authorities and other public health partners inside and outside the sector to facilitate execution of the technical cooperation program.
- Modernisation of human and financial resource management for greater profitability, combining the streamlining of administrative processes, transparency, and co-management.
2. EPIDEMIOLOGY, DISEASE PREVENTION AND CONTROL
PURPOSE
To improve national capacity at all levels for health situation analysis and the prevention and control of risks and threats to individuals, families, and the community.
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Focused decision-making in the health sector, essentially through the use of complete, timely, and high-quality health information.
- Methods and technologies transferred to the decentralized levels of the national public health laboratory network.
- National capacity strengthened for the surveillance, prevention, and control of priority diseases.
- Strategies strengthened for the control and prevention of priority diseases, epidemiological and operations research on the impact of these strategies, and evaluation of their effectiveness and efficiency.
- Access to pertinent health information facilitated; educational and mass communication material, as well as selected bibliographies, prepared and distributed.
3. POLICIES, HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES SYSTEMS
PURPOSE
To strengthen the capacity of the organisation to implement health policies, organise and manage the health system, and develop human resources.
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Public health planning methods and instruments validated and promoted at the national, regional and local levels within the framework of the National Coordinated and Decentralised Public Health System, using a participatory approach.
- Policies, standards, strategies, methods, and instruments for improving the organization, management, and quality of health services designed and disseminated.
- Human Resources Development Institute strengthened in terms of its management, regulatory, and design role, within the framework of the National Coordinated and Decentralised Public Health System; and strategies, methods, and instruments disseminated for training, managing, and improving the performance of human resources in the health sector.
- Contribution toward better institutional and sectoral financial management in public health.
- Strategies established for expanding social protection in health, with view to eliminating exclusion in health insurance and providing access to quality health services.
- Official regulatory agency for pharmaceutical products strengthened, with emphasis on selection and quality monitoring, and plans of action implemented to promote equitable access to drugs and their rational use.
4. HEALTH PROMOTION
PURPOSE
To strengthen health-promotion campaigns with an equity approach.
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Healthy environmental policies, projects, programs, and networks established in municipalities, schools, and families.
- Policies, programs, and standards clearly established to produce positive changes in the physical, nutritional, and mental health of the population in terms of habits and lifestyles.
- Policies, programs, and regulations established, aimed at comprehensively promoting human development, with a life cycle approach.
- Production and inter-sectoral dissemination of information and knowledge on differences and inequities between men and women in health sector reform; providing an institutional framework for the approach to promote equity between men and women in health policies and surveillance systems.
- Public health communication and information strategies developed to encourage healthy behaviour in the population.
5. HEALTH AND THE ENVIRONMENT, DISASTER PREVENTION AND MITIGATION
PURPOSE
To strengthen national and regional capacity for the management of environmental health and water and sanitation services, and for the organization, prevention, and mitigation of emergencies and disasters
EXPECTED RESULTS
- National strategy for environmental health, occupational health, and disaster prevention and mitigation formulated and integrated into public health policies, coordinating with other competent agencies to ensure their coherent application.
- Steering role of the organisation consolidated in environmental and occupational health and disaster prevention and mitigation.
- National surveillance system for environmental and occupational health and natural phenomena consolidated for the identification and control of health risks to facilitate policy-making at the national and regional levels; national and international communication system established for the dissemination of scientific, technical and legislative information on environmental and occupational health.
- Human resources capacity to produce high-quality environmental and occupational management strengthened.
- National strategy established in the sanitation subsector that will help to modernise its management, achieve the financial viability of service providers, and improve access to services as well as their quality and sustainability.
6. TECHNICAL COOPERATION AMONG COUNTRIES
PURPOSE
To promote collective self-sufficiency through the building of national capacity and the willingness to share it for the common good
EXPECTED RESULTS
- Cooperation carried out for health monitoring, disease prevention and control, health promotion, environmental health, and the organization of health services.
RESOURCES (USD)
AHO BENIN BUDGET 2020 (USD million)* based on 2017 pop 11.18 million World Bank
| SO | BUDGET ITEM | AMOUNT* |
| 1 | Combating communicable diseases | 186 |
| 2 | Tackling non communicable diseases | 207 |
| 3 | Addressing determinants of health & risk factors | 180 |
| 4 | Modernising health system and health service | 185 |
| 5 | Improving preparedness, surveillance and response | 180 |
| 6 | Developing good governance & corporate services | 180 |
| Total | 1,118 |
AHO estimates that it needs to spend at least USD100 per capita on health to meet the basic health needs of the people in Africa. This is too far below developed countries e.g. in England it is US$1,300 per capita (2018)

